- July 31, 2023Announcement
NeurIPS 2023 Competition Track: Big-ANN
- October 12, 2022Research
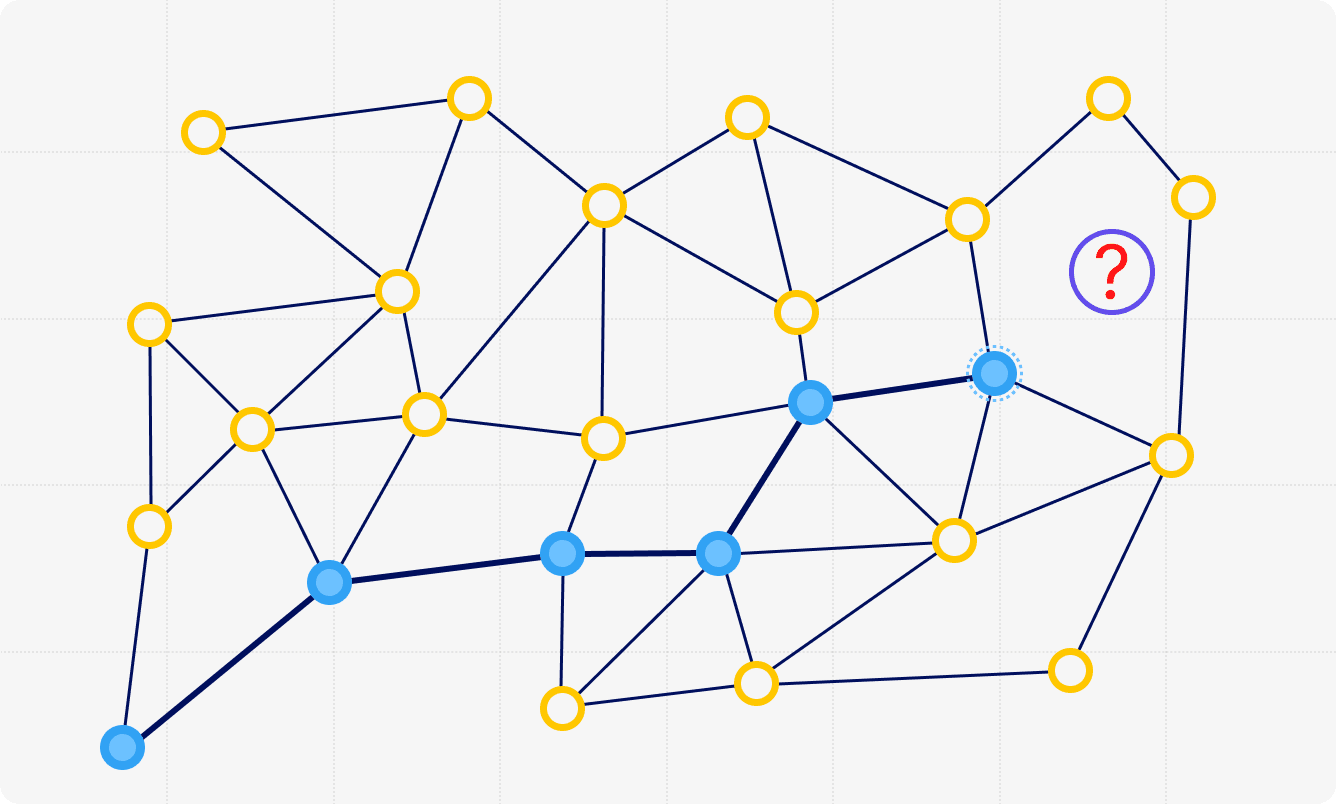
Graph-based nearest neighbor search
- April 26, 2021Research
Benchmarks for Billion-Scale Similarity Search
Nearest neighbor search
Nearest neighbor search is a long-standing problem arising in a large number of machine learning applications, such as recommender services, information retrieval, and others.
Posts
Publications
Results of the Big ANN: NeurIPS’23 competition
NeurIPS Datasets and Benchmarks, 2025The 2023 Big ANN Challenge, held at NeurIPS 2023, focused on advancing the state-of-the-art in indexing data structures and search algorithms for practical variants of Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) search that reflect its the growing complexity and diversity of workloads. Unlike prior challenges that emphasized scaling up classical ANN search (Simhadri et al., NeurIPS 2021), this competition addressed sparse, filtered, out-of-distribution, and streaming variants of ANNS. Participants developed and submitted innovative solutions that were evaluated on new standard datasets with constrained computational resources. The results showcased significant improvements in search accuracy and efficiency, with notable contributions from both academic and industrial teams. This paper summarizes the competition tracks, datasets, evaluation metrics, and the innovative approaches of the top-performing submissions, providing insights into the current advancements and future directions in the field of approximate nearest neighbor search.
DeDrift: Robust Similarity Search under Content Drift
ICCV, 2023The statistical distribution of content uploaded and searched on media sharing sites changes over time due to seasonal, sociological and technical factors. We investigate the impact of this "content drift" for large-scale similarity search tools, based on nearest neighbor search in embedding space. Unless a costly index reconstruction is performed frequently, content drift degrades the search accuracy and efficiency. The degradation is especially severe since, in general, both the query and database distributions change. We introduce and analyze real-world image and video datasets for which temporal information is available over a long time period. Based on the learnings, we devise DeDrift, a method that updates embedding quantizers to continuously adapt large-scale indexing structures on-the-fly. DeDrift almost eliminates the accuracy degradation due to the query and database content drift while being up to 100x faster than a full index reconstruction.
Graph-based Nearest Neighbor Search in Hyperbolic Spaces
ICLR, 2022The nearest neighbor search (NNS) problem is widely studied in Euclidean space, and graph-based algorithms are known to outperform other approaches for this task. However, hyperbolic geometry often allows for better data representation in various domains, including graphs, words, and images. In this paper, we show that graph-based approaches are also well suited for hyperbolic geometry. From a theoretical perspective, we rigorously analyze the time and space complexity of graph-based NNS, assuming that an n-element dataset is uniformly distributed within a d-dimensional ball of radius R in the hyperbolic space of curvature -1. Under some conditions on R and d, we derive the time and space complexity of graph-based NNS and compare the obtained results with known guarantees for the Euclidean case. Interestingly, in the dense setting (d << log(n)) and under some assumptions on the radius R, graph-based NNS has lower time complexity in the hyperbolic space. This agrees with our experiments: we consider datasets embedded in hyperbolic and Euclidean spaces and show that graph-based NNS can be more efficient in the hyperbolic space. We also demonstrate that graph-based methods outperform other existing baselines for hyperbolic NNS. Overall, our theoretical and empirical analysis suggests that graph-based NNS can be considered a default approach for similarity search in hyperbolic spaces.
Datasets
Text-to-Image dataset for billion-scale similarity search
Yandex Text-to-Image (T2I) dataset is collected to foster the research in billion-scale nearest neighbor search (NNS) when query distribution differs from the indexing one. In particular, this dataset addresses the cross-domain setting: a user specifies a textual query and requests the search engine to retrieve the most relevant images to the query. Notably, current large-scale indexing methods perform poorly in this setting. Therefore, novel highly-performant indexing solutions robust to out-of-domain queries are in high demand.
The dataset represents a snapshot of the Yandex visual search engine and contains 1 billion 200-dimensional image embeddings for indexing. The image embeddings are produced by the Se-ResNext-101 model. The embeddings for textual queries are extracted by a variant of the DSSM model.
Read more about the data format and how to download the dataset in the related post.